
SQ001
For Rapid detection of Salmonella species including S. typhi, S. paratyphi and Salmonella lactose positive strains
Package size: 1000 ml
DKK 750,00
DKK 2.250,00
Not in stock, delivery 1-2 weeks
Chromogenic medium for detection and enumeration of Bacillus cereus group in environmental and food samples.
The product is composed of a powder base (B) and 1 supplement (S).
MEDIUM PERFORMANCE:
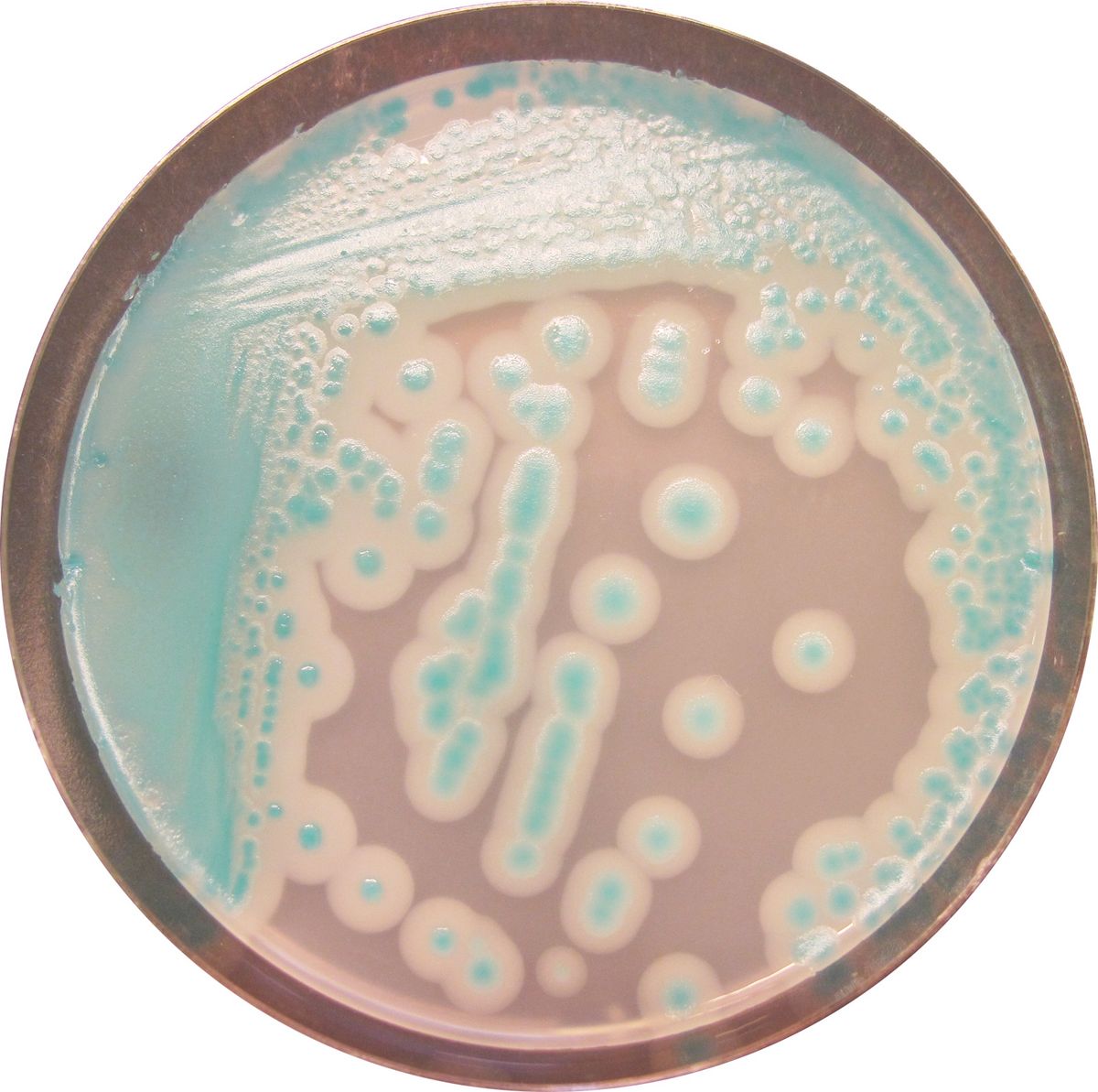
1. Easy reading: Only 24 h incubation at 30 °C. The intense blue colored colonies on a translucent agar facilitates the reading compared to Mannitol based agar which displays red colonies on pink agar.
2. Simplicity: Contrary to MYP or Mossel agar, there is no need to add the tedious Egg york emulsion.
3. Highly sensitive & specific for cereus group compared to MYP or Mossel agar.
The classical MYP or Mossel agar rely on the inability of B. cereus to utilise the mannitol, which renders the plate reading difficult in the presence of abundant flora. CHROMagar™ B.cereus, owe to the chromogenic technology, overcomes this difficulty. 100 % Sensitivity / 100 % Specificity *
* Specificity and sensitivity from scientific study : Adria Normandie Study, 2012
4. Better selectivity & recovery compared to classical medium agar.
5. Longer prepared plate shelflife compared to MYP and Mossel agar which are only 5 days shelflife.
TYPICAL APPEARANCE OF MICROORGANISMS:
Bacillus cereus → blue with white halo
Other Bacillus → blue, colourless or inhibited
Gram negative bacteria → inhibite
Yeast and moulds → inhibited
Bacillus cereus is a spore-forming bacterium that can be frequently isolated from soil and some food which produces toxins. These toxins can cause two types of illness: one type characterized by diarrhea (long incubation, 8-16 hours) and the other by nausea and vomiting (short incubation, 1-6 hours). The short-incubation form is most often associated with rice dishes that have been cooked and then held at warm temperatures for several hours. The long-incubation form of B. cereus is frequently associated with meat or vegetable containing foods, after cooking. The bacterium has been isolated from dried beans and cereals, and from dried foods such as spices, seasoning mixes and potatoes.